+91 755 669 1338
+91 755 669 1338
 abhijit@iiserb.ac.in
abhijit@iiserb.ac.in
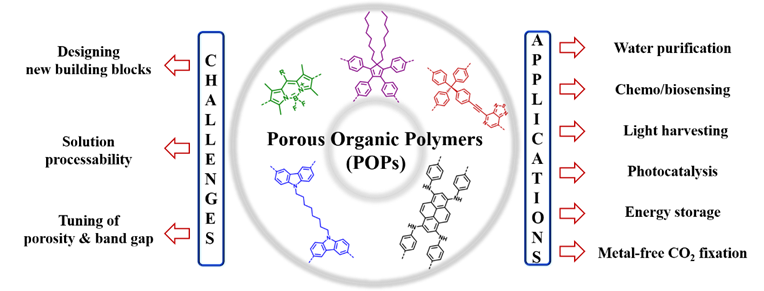
Porous organic materials have attracted significant attention in the last few years due to their high surface area and functionalizable pores. Superior thermal, hydrothermal and chemical stability due to strong covalent bonds and presence of light weight elements like Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen etc makes it a suitable candidate for various multi farious applications. The tunable pore size with the high surface area as well as excellent structural robustness trigger their extensive utilization from the gas storage and separation to heterogeneous catalysis and water purification. Amidst all the advantages, the judicious inclusion of pi-electron conjugation in the network makes the conjugated porous organic polymer (CPOPs) unique from all other porous materials. Hence, CPOPs became popular for their multimodal applications like sensing, light harvesting, photocatalysis and energy storage. In this present scenario of the field, our group took up the problem to meet various challenges like designing the task-specific building blocks, tuning the band gap and porosity and most importantly development of POPs with solution processability. Along with the design strategy, we have also demonstrated the efficacy of POPs in diverse applications ranging from chemo/ biosensing, light harvesting, energy storage, photocatalysis, to metal-free CO2 fixation.
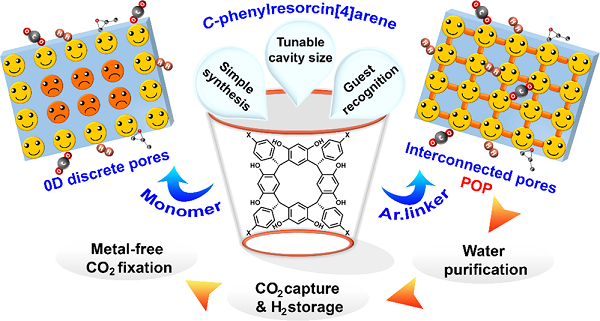
Molecular hosts, like, cavitands, capsules, cages, the ‘Lego’ blocks of supramolecular chemistry, having aesthetically appealing architecture, possess large cavities to accommodate small molecules or ions. The confined space of these molecular hosts with excellent guest recognition property lead to multifarious applications ranging from catalysis, molecular separation, sensing, enzyme mimetic catalysis, to the development of artificial molecular machines.In our lab we focus on fabricating materials which can exhibit the charecateristics of both the cavitands as well a Porous Organic Polymer through intercating cavitands as a monomeric unit in the polymeric framework.
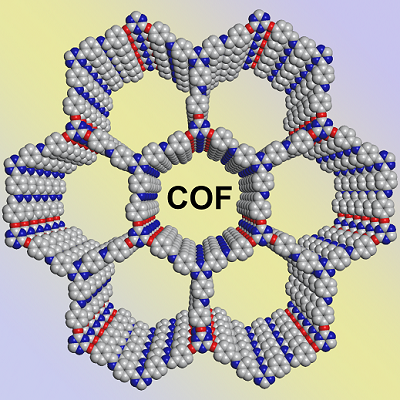
Covalent Organic Frameworks are an emerging class of Porous Organic Materials. Due to their ordered structure and dynamic covalent chemistry of their synthesis, the materials are crystalline and have a well-defined pore structure. In our lab, we focus on designing 2D-COF for various applications particularly energy storage and water purification.