Welcome to RKM Research Group
Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) BhopalAbout Us
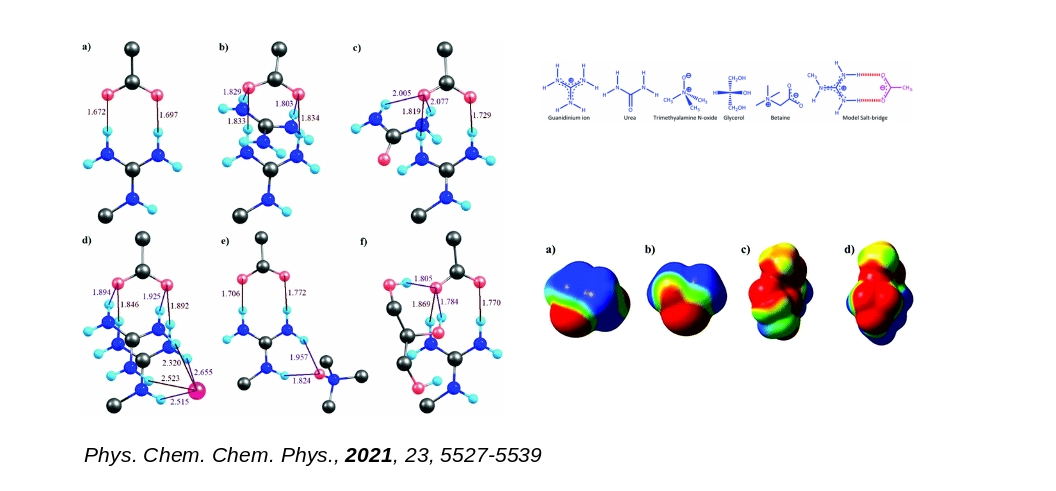
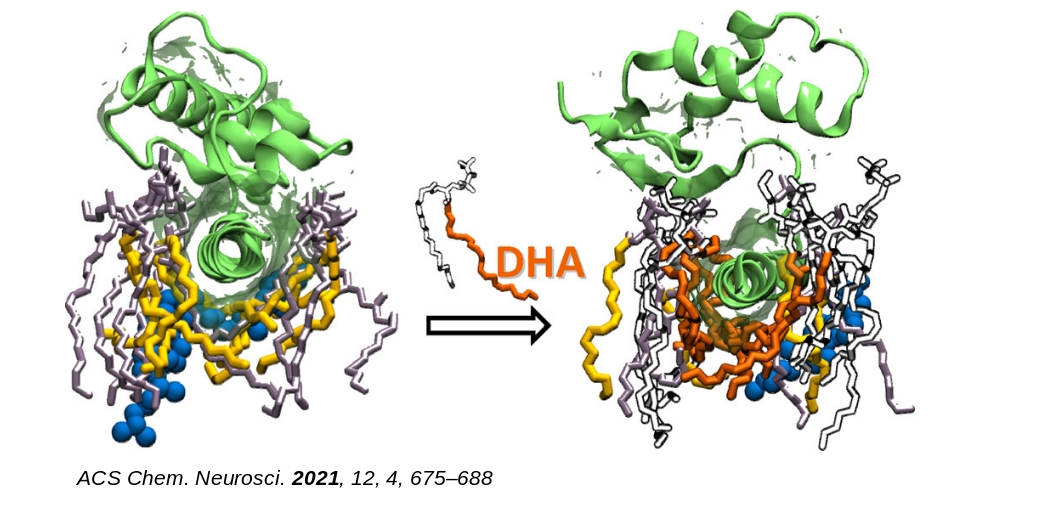
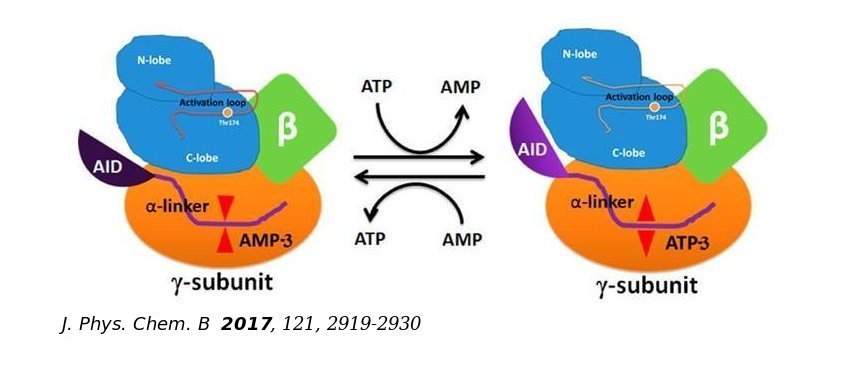
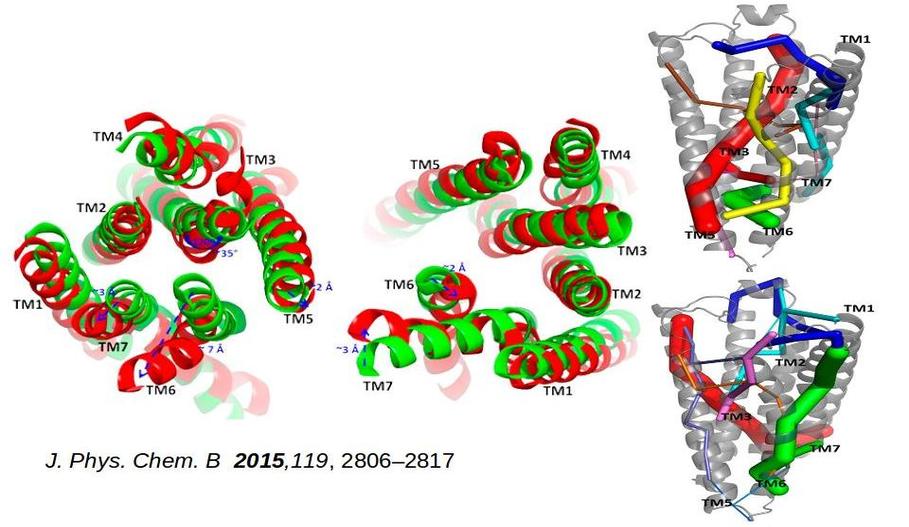
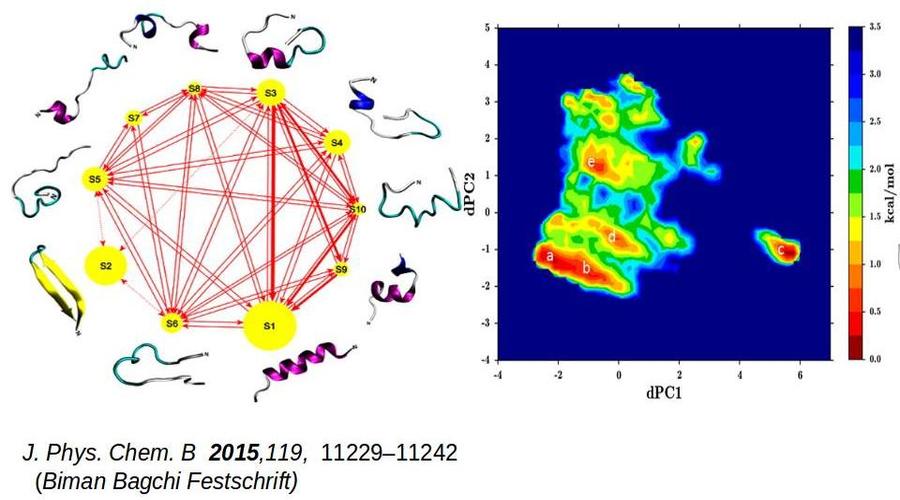
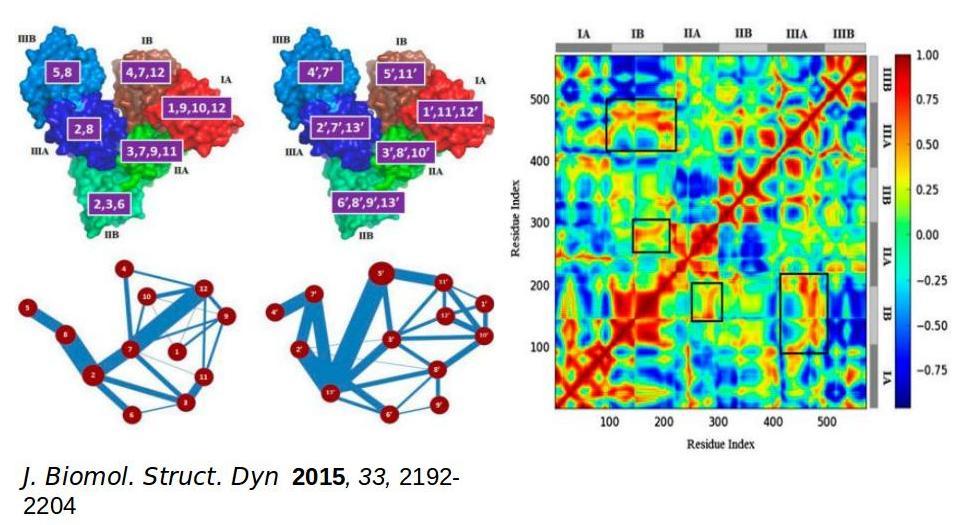
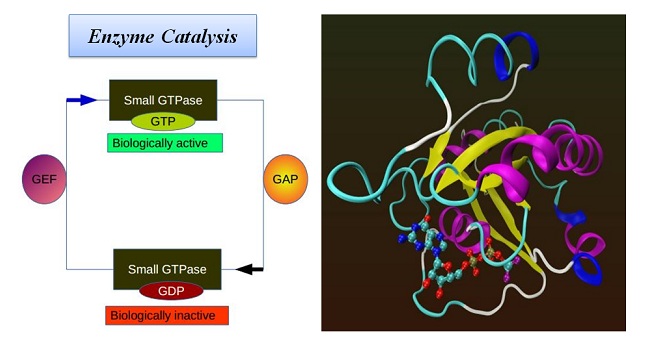
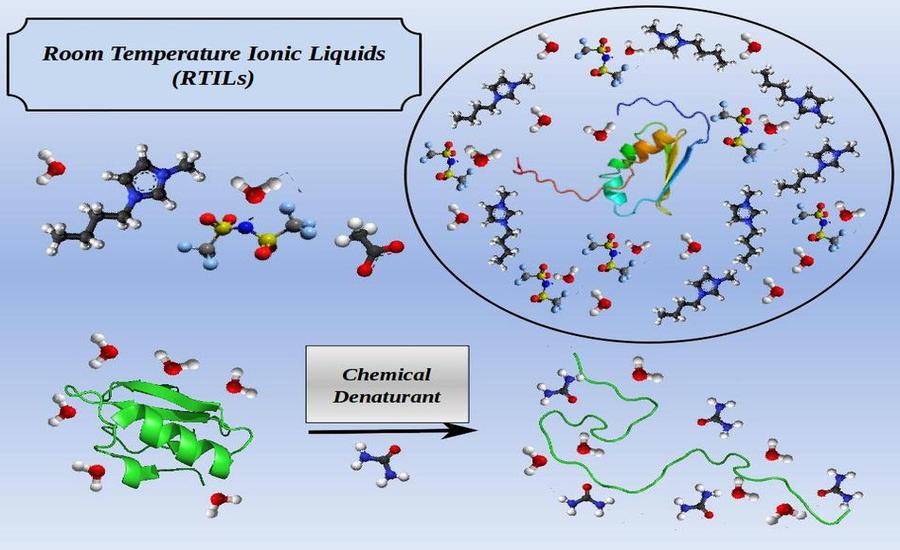
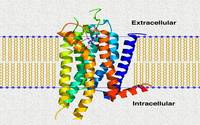
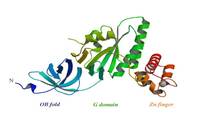
Our research program aims at understanding of the microscopic correlations between structure, conformational dynamics (operating at different length and time scales) and functions of biomolecules using a combination of state-of-the-art computer simulation methods based on principles of statistical mechanics and quantum chemistry, and machine learning techniques.
Recent News: