contribution to scientific community
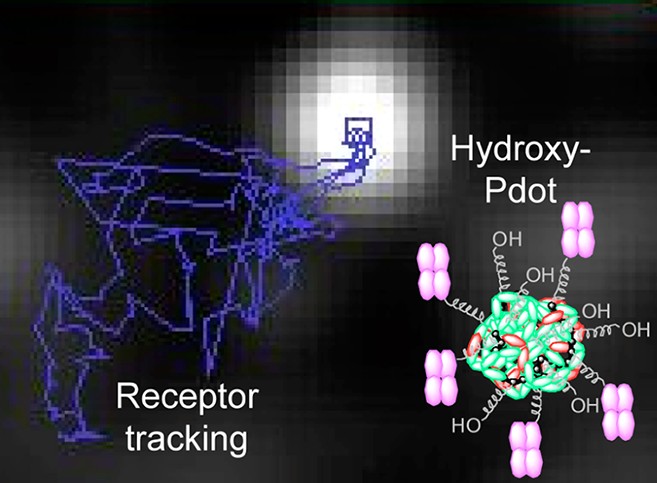
Abstract: Fluorescent nanoparticles have enabled many discoveries regarding howmolecular machines function. Quantum dots have been the dominant class of fluorescent nanoparticles but suffer from blinking and from a substantial dark fraction; particles where the fluorescence is never seen; complicating any analysis of biological function. Nanoparticles composed of conjugated fluorescent polymers (Pdots) have recently been shown to have high brightness and no blinking. Here we develop a robust and efficient means to measure the dark fraction of Pdots, conjugating Atto dyes to the nanoparticles and testing fluorescence colocalization of dye and Pdot puncta. This established that the Pdots we generated had minimal dark fraction: ~3%. The application of nanoparticles in biological environments is highly sensitive to surface functionalization. For Pdots we found that passivation with uncharged hydroxy-terminated polyethylene glycol caused adramatic reduction in nonspecific cell binding and aggregation compared to a charged coating. Using carbonyl di-imidazole the hydroxy-Pdots were functionalized efficiently with streptavidin for high stability targeting, allowing specific labeling of mammalian cells. Type I insulin-like growth factorreceptor (IGF1R) regulates cell survival and development, with roles in aging, heart disease, and cancer. We used hydroxy-Pdots to track the dynamics ofIGF1R on a breast cancer cell-line, determining the diffusion characteristics and showing cholesterol-containing membrane nanodomains were importantfor receptor mobility at the plasma membrane. The near-unity bright fraction and low nonspecific binding of hydroxy-Pdots, combined with Pdotphotostability and lack of blinking, provides many advantages for investigations at the single molecule level.
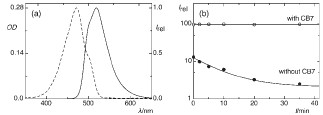
Abstract: When included in a supramolecular barrel with transition-metal ions as lids, bicyclic azoalkanes undergo phase-selective photolysis to afford new photoproducts and photoproduct distributions. In the presence of the macrocycle cucurbit[7]uril and Ag+ ions, 2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene forms a ternary host–guest inclusion complex in which the cations are coordinated to the carbonyl rims of the host. Direct photolysis of this ternary complex provides cyclopentene as a new photoproduct.
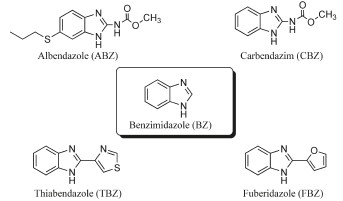
Abstract: UV–vis and NMR spectroscopic techniques were employed to demonstrate the ability of the synthetic macrocy- clic host cucurbit[7]uril (CB7) to solubilize and stabilize widely used fungicides and anthelmintic drugs of the benzimida- zole family in water, namely, albendazole (ABZ), carbendazim (CBZ), thiabendazole (TBZ),fuberidazole (FBZ), and the parent benzimidazole (BZ). CB7 binds the protonated forms of these guests very strongly (e.g., K = 2.6 Â 107 L/mol for ABZ) but their neutral forms significantly more weakly (e.g., K = 6.5 Â 104 L/mol for ABZ), which reflects a complexa- tion-induced increase of their pKa values by 2.6 units for ABZ, 2.5 units for CBZ, 4.0 units for TBZ, 3.8 units for FBZ, and 3.5 units for BZ. The absolute drug solubilities increased upon complexation from 0.003 to 0.300 mmol/L for ABZ, from 0.160 to 1.12 mmol/L for CBZ, from 0.110 to 1.11 mmol/L for TBZ, and from 0.25 to 0.75 mmol/L for FBZ (for BZ, the solubility enhancement was found to be insignificant). Complexation by CB7 further improves the photostability of the drugs and alters their photophysical properties.
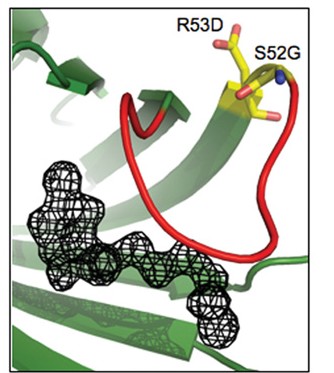
Abstract: The interaction between SA (streptavidin) and biotin is one of the strongest non-covalent interactions in Nature. SA is a widely used tool and a paradigm for protein–ligand interactions.We previously developed a SA mutant, termed Tr (traptavidin), possessing a 10-fold lower off-rate for biotin, with increased mechanical and thermal stability. In the present study, we determined the crystal structures of apo-Tr and biotin–Tr at 1.5 Å resolution. In apo-SA the loop (L3/4), near biotin’s valeryl tail, is typically disordered and open, but closes upon biotin binding. In contrast, L3/4 was shut in both apo-Tr and biotin–Tr. The reduced flexibility of L3/4 and decreased conformational change on biotin binding provide an explanation for Tr’s reduced biotin off- and on-rates. L3/4 includes Ser45, which forms a hydrogen bond to biotin consistently in Tr, but erratically in SA. Reduced breakage of the biotin–Ser45 hydrogen bond in Tr is likely to inhibit the initiating event in biotin’s dissociation pathway. We generated a Tr with a single biotin-binding site rather than four, which showed a similarly low off-rate, demonstrating that Tr’s low off-rate was governed by intrasubunit effects. Understanding the structural features of this tenacious interaction may assist the design of even stronger affinity tags and inhibitors.
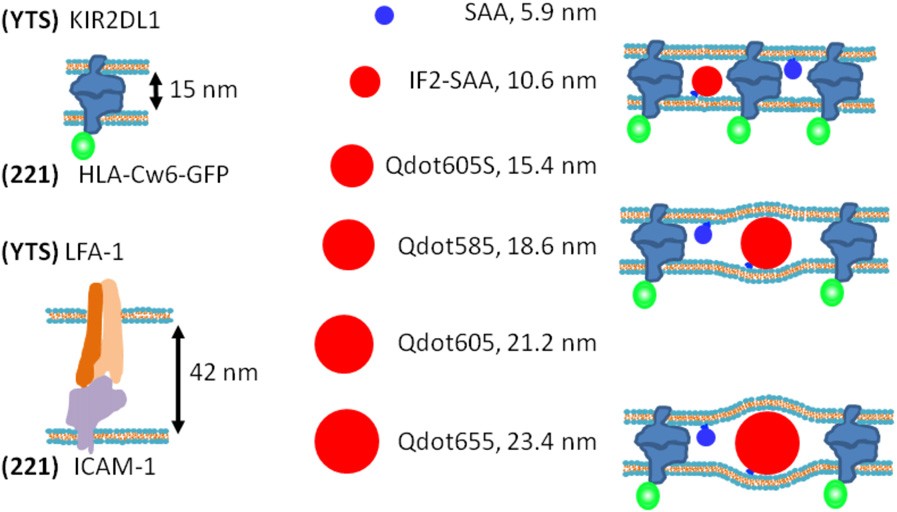
Abstract: Immunological synapses are specialized intercellular contacts formed by several types of immune cells in contact with target cells or antigen-presenting cells. A late-stage immune synapse is commonly a bulls-eye pattern of immune cell receptor-ligand pairs surrounded by integrin complexes. Based on crystal structures, the intermembrane distance would be ~15 nm for many immune cell receptor-ligand pairs, but ~40 nm for integrin-ligand pairs. Close proximity of these two classes of intermembrane bonds would require significant membrane bending and such proteins can segregate according to their size, which may be key for receptor triggering. However, tools available to evaluate the intermembrane organization of the synapse are limited. Here, we present what we believe to be a novel approach to test the importance of size in the intercellular organization of proteins, using live-cell microscopy of a size-series of fluorescently-labeled molecules and quantum dots to act as molecular rulers. Small particles readily colocalized at the synapse with MHC class I bound to its cognate natural killer cell receptor, whereas particles larger than 15 nm were increasingly segregated from this interaction. Combined with modeling of the partitioning of the particles by scaled-particle adsorption theory, these molecular rulers show how membrane-bending elasticity can drive size-dependent exclusion of proteins within immune synapses.
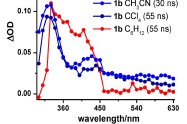
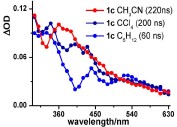
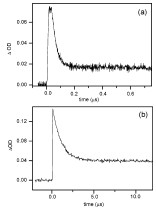
Abstract: The steady-state as well as transient absorption spectroscopy of a series of 2-bromo aryl ketones have been comprehensively examined to gain insights concerning (i) the transient phenomena (absorption spectral attributes as well as lifetimes), (ii) rates of C–Br homolysis, and (iii) the behavior of 2-aroylaryl radicals thus generated. The X-ray crystal structure analyses of selected ketones in which the mesomeric effects operate differently reveal that the two aryl rings are drastically twisted about the C=O bond. The twisting man- ifests itself in the spectral features of the transients, attributed to triplet–triplet (T–T) absorp- tions, such that they are not readily comparable in some cases to the transients of parent diaryl ketones that lack the 2-bromo group. By associating triplet decays with C–Br cleavage rates, the absolute rate data have been determined for diverse 2-bromoaryl ketones. With the exception of 2-bromo ketones containing meta-methoxy substituents, all other ketones are found to undergo efficient C–Br bond cleavage with rates of ca. 0.1–1.0 × 108 s–1. For m-methoxy-substituted ketones, intriguingly slower deactivation of the triplets was observed. Based on solvent-dependent variation of the lifetimes (longer lifetimes in polar solvents), intramolecular charge transfer has been proposed. The preparative photochemistry and tran-sient phenomena permit invaluable inferences as to the reactivity of 2-aroylaryl radicals in general. Quantum yield determinations and product analyses reveal that highly electrophilic aryl radicals undergo radical recombination, in a poor hydrogen-donating solvent, almost exclusively (>90 %) in the absence of incentive for stabilization via conversion to p-conju- gated hydrofluorenyl radicals. Of course, when the latter is feasible, Pschorr cyclization leads to productive photochemical outcome. Moderately electrophilic radicals that lack stabiliza- tion via conversion to hydrofluorenyl radicals lend themselves to intramolecular 1,5-hydro- gen shifts in conjunction with the formation of dehalogenated diaryl ketones and cyclized fluorenones (Fls) or its analogs.
Abstract: A ready synthetic accessibility of a series of 6- and 7-arylchromenes via Pd0-catalyzed Suzuki coupling protocol has permitted a comprehensive investigation of the thermal decay behavior of a broad set of photogenerated o-quinonoid reactive intermediates. It is shown that substantial mesomeric effect between the benzopyran nucleus and the aryl ring at C6 or C7 position of the former renders significant absorption beyond 350 nm such that they are readily photoactivated to yield colored o-quinonoid intermediates. The absorption spectra of the latter are found to be strongly influenced by the substituents on C2-, C6- and C7-aryl rings; indeed the colored absorptions can be conveniently tuned by appropriate choice of substituents. The thermal decay (bleaching phenomenon), which is important from the point of view of their application in ophthalmic lenses, was investigated in each case by ms–ms as well as real-time absorption spectroscopy. By careful experimentation, we have extracted the decay rate constants for Z,E and E,E o-quinonoid isomers of all 6- and 7-arylchromenes in an attempt to establish a correlation between the electronic attributes with their thermokinetic behavior. From a combined analysis of ms–ms (laser flash) and real-time kinetic data, it is shown that the colored o-quinonoid intermediates decay faster when the C2- aryl and C6-/C7-aryl rings contain electron- donating and electron-accepting groups, respectively. In the same vein, the decay was found to occur slowly for the reversed scenario, while intermediate decay rates are observed when both substituents are electron-donating. Thus, any substituent on the C2-aryl ring that contributes mesomerically to the development of charge on the quinonoid oxygen, and any substituent on the C6-/C7-aryl ring that exerts �I effect appear to expedite thermal decay. Furthermore, evidence is obtained for the first time from ms timeresolved laser-flash spectroscopy for the formation and characterization of the trans,cis (E,Z) o-quinonoid isomer,which has heretofore eluded spectral characterization in the photochromic phenomena of pyrans.
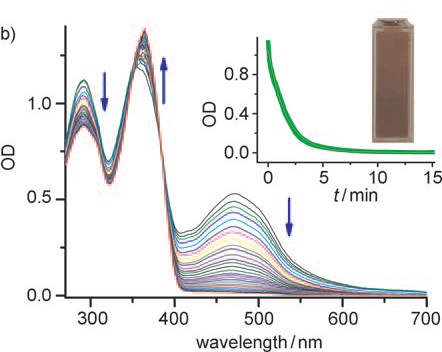
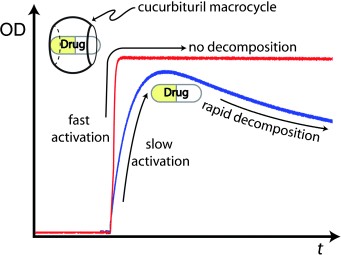
Abstract: UV and NMR spectroscopic studies show that drugs such as omeprazole and lansoprazole, popular drugs for the treatment of gastric acid related diseases, are stable for several weeks by using cucurbit[7]uril as a macrocyclic host. The drugs are also more rapidly converted into their active forms by an acid-promoted reaction catalyzed by a supramolecular pKa shift.
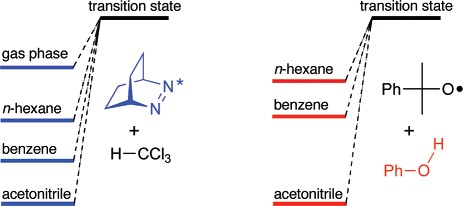
Abstract: Kinetic solvent effects on hydrogen abstractions, namely, acceleration in nonpolar solvents, have been presumed to be restricted to O-H hydrogen donors. We demonstrate that also abstractions from C-H and even Sn-H bonds by cumyloxyl radicals and n,ð*-excited 2,3-diazabicyclo-[2.2.2]oct-2-ene are fastest in the gas phase and nonpolar solvents but slowest in acetonitrile. Accordingly, solvent effects on hydrogen abstractions are more general, presumably due to stabilization of the reactive oxygen or nitrogen species in polar solvents.
Abstract: A water-soluble supramolecular sensing assembly, composed of an imidazolium-substituted calix[4]arene and a fluorescent aminodiacetate derivative of 1,8-naphthalimide, was studied. Addition of citrate led to a large fluorescence enhancement, while tartrate, acetate, as well as selected inorganic anions gave smaller effects. The sensing principle and selectivity for citrate rely on the formation of a ternary fluorophore- host-anion complex and complexation-induced pKa shifts of an amino group attached to the fluorophore. The complexation of citrate induces a protonation of the amino group, which switches off intramolecular photoinduced electron transfer as the fluorescence quenching pathway, leading to an enhancement of the optical output signal. The intricate sensor principle was corroborated by pH titrations, binding constants, and structural information as obtained by 1H NMR spectroscopy.
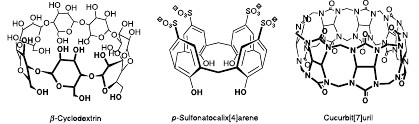
Abstract: The potential of cucurbiturils, water-soluble macrocyclic host molecules composed of glycoluril units, for tuning the properties of fluorescent dyes and advancing new applications is illustrated. Cucurbit[7]uril (CB7), which presents a particularly attractive derivative due to its intermediary size and high water solubility, has been shown to display a variety of advantageous effects on fluorescent dyes, which include increased fluorescence intensity and brightness, enhanced photostability, protection towards fluorescence quenchers, solubilization, and deaggregation. Particularly noteworthy is the prolongation of the fluorescence lifetimes of different dyes, which can be traced back to the low polarizability of the host cavity. In addition, the host serves as cation receptor, which causes a considerable shift of protonation equilibria and assists the protonation of fluorescent dyes. The latter effect can be exploited in the design of protolytic fluorophore displacement assays. The perspective of cucurbiturils as stabilizers for laser dyes, enhancement agents in time-resolved fluorescence (TRF) assays, contrast agents for fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM), and dyes for fluorescent collectors for
solar cells is mentioned. Original experimental results for the effect of CB7 on the fluorescence properties of three dyes (Macrolex Yellow 10 GN, Dapoxyl, and 4-(dimethylamino) benzonitrile) are presented.
Abstract: Ternary complexes formed from a macrocyclic host (p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene), an organic guest (2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-2-ene), and transition-metal ions result in a host-assisted formation of a metal–ligand bond. The system displays a very high selectivity as a result of triple supramolecular recognition involving Coulombic interactions, hydrophobic guest binding, and weak metal–ligand interactions.
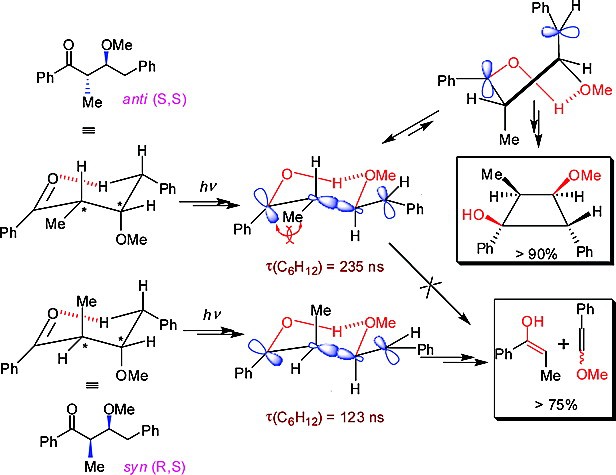
Abstract: The photoreactivity and nanosecond transient phenomena have been investigated for a rationally designed set of ketones 4-9 in order to gain comprehensive insights concerning the influence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding on (i) the lifetimes of triplet 1,4-biradicals and (ii) the partitioning of the latter between cyclization and elimination. Comparisons of the photochemical results and lifetime data for the biradicals of ketones 6 versus 8 and 7 versus 9 revealed a remarkable influence of hydrogen bonding when superimposed upon steric factors: while 6 and 7 yielded cyclobutanols in poor yields, cyclization was found to be overwhelmingly predominant for 8-anti and moderately so for 9-anti, with a high stereoselectivity in the formation of cyclobutanols (>95% for 8-anti). The diastereochemistry in the case of 8 permitted the occurrence of fragmentation or cyclization almost exclusively (>90% cyclization for 8-anti and >75% elimination for 8-syn). Significantly, the intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the biradicals of 8 and 9 was found to reverse their partitioning between cyclization and elimination compared with the behavior of the biradicals of ketones 3; the ketones 8-anti and 9-anti underwent cyclization in benzene, predominantly leading to cyclobutanols with syn stereochemistry between the C2 and C3 substituents. In accordance with photoproduct profiles, an unprecedented 2-fold difference in the lifetimes of the intermediate diastereomeric triplet biradicals of ketones 8 in nonpolar solvents (e.g., τsyn = 123 ns and τanti = 235 ns in cyclohexane) was observed via nanosecond laser flash photolysis, while no such difference in lifetimes was found for the triplet biradicals of acetoxy ketones 9. The intriguing diastereodifferentiation in the lifetimes of the diastereomeric triplet 1,4-biradicals of 8 and the product profiles of ketones 6, 7, and 9 are best reconciled via a unified mechanistic picture in which superposition of steric factors over varying magnitudes of O-H···O hydrogen bonding selectively facilitates a particular pathway. In particular, the diastereodifferentiation in the photochemical outcomes for the diastereomers of ketone 8 and in the lifetimes of their triplet biradicals can be understood on the basis of rapid deactivation of the 8-syn triplet biradical via fragmentation and slow cyclization of the 8-anti triplet biradical from chair- and twist-boat-like hydrogen-bonded conformations, respectively. The photolysis in polar aprotic solvents such as DMSO and pyridine was found to reverse the chemoselectivity, yielding reactivity paralleling that of ketones 3, for which the steric factors between the C2 and C3 substituents control the photochemical outcome.
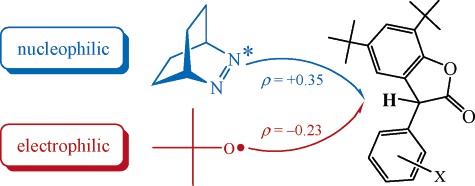
Abstract: 5,7-Di-tert-butyl-3-aryl-3H-benzofuran-2-ones are lactones with potential antioxidant activity, owing to their abstractable benzylic C-H hydrogens. The fluorescence quenching of the azoalkane 2,3-diazabicyclo- [2.2.2]oct-2-ene (DBO), an established probe for the hydrogen-donor propensity of chain-breaking antioxidants, was investigated for 16 aryl-substituted benzofuranone derivatives [m,m-(CF3)2, p-CN, m-CN, p-CF3, p-COOCH3, m-CF3, p-Cl, p-F, H, m-CH3, p-CH3, m,p-(CH3)2, p-OCH3, o-CH3, o-CF3, o,m-(CH3)2]. Analysis of the rate data in terms of a linear free energy relationship yielded a reaction constant of F ) +0.35. This implies that n,ð*-excited DBO acts as nucleophilic species. In contrast, hydrogen abstraction of tert-butoxyl radicals from the benzofuranones was accelerated by electron-donating substituents (F ) -0.23), in conformity with the electrophilic character of oxygen-centered alkoxyl radicals. Possible implications for the optimization of the hydrogen-donor propensity of antioxidants through structural variation are discussed.
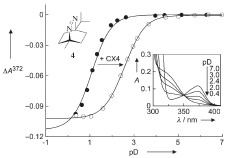
Abstract: The pD dependence of the complexation of p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene (CX4) with the azoalkanes 2,3- diazabicycloACHTUNGTRENUNG[2.2.1]hept-2-ene (1), 2,3-
diazabicycloACHTUNGTRENUNG[2.2.2]oct-2-ene(2),2,3-diazabicycloACHTUNGTRENUNG[2.2.3]non-2-ene (3), and 1- methyl-4-isopropyl-2,3-diazabicyclo- ACHTUNGTRENUNG[2.2.2]oct-2-ene (4) in D2O has been studied. The pD-dependent binding constants, determined by 1H NMR spectroscopy, were analyzed according to a seven-state model, which included the CX4 tetra- and penta-anions, the protonated and unprotonated forms of the azoalkanes, the corresponding complexes, as well as the complex formed between CX4 and the deuteriated hydronium ion. The variation of the UV absorption spectra, namely the hypsochromic shift in the near-UV band of the azo chromophore upon protonation,was analyzed according to a fourstate model. Measurements by independent methods demonstrated that complexation by CX4 shifts the pKa values of the guest molecules by around 2units , thereby establishing a case of host-assisted guest protonation. The pKa shift can be translated into improved binding (factor of 100) of the protonated guest relative to its unprotonated form as a result of the cationreceptor properties of CX4. The results are discussed in the context of supramolecular catalytic activity and the pKa shifts induced by different types of macrocyclic hosts are compared.
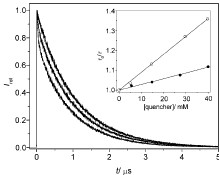
Abstract: The stereochemistry at C2 and C3 carbons controls the partitioning of triplet 1,4-biradicals of ketones 2 among various pathways. Differences in the major reaction pathways, for example, cyclization (syn) and fragmentation (anti), adopted by the diastereomeric 1,4-radicals of ketones 2 have permitted unprecedented diastereomeric discrimination in their lifetimes to be observed by nanosecond laser flash photolysis. From quantum yield measurements and transient lifetime data, the absolute rate constants for cyclization and fragmentation of a pair of diastereomeric triplet 1,4-biradicals have been determined for the first time.
Abstract: The fluorescence quenching of singlet-excited 2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-2-ene (DBO) by 22 phenols and 12 alkylbenzenes has been investigated. Quenching rate constants in acetonitrile are in the range of 108–109 M-1 s-1 for phenols and 105–106 M-1s-1 for alkylbenzenes. In contrast to the quenching of triplet-excited benzophenone, no exciplexes are involved, so that a pure hydrogen atom transfer is proposed as quenching mechanism. This is supported by (1) pronounced deuterium isotope effects (kH/kDca 4–6), which were observed for phenols and alkylbenzenes, and (2) a strongly endergonic thermodynamics for charge transfer processes (electron transfer, exciplex formation). In the case of phenols, linear free energy relationships applied, which led to a reaction constant of ?=–0.40, suggesting a lower electrophilicity of singlet-excited DBO than that of triplet-excited ketones and alkoxyl radicals. The reactivity of singlet-excited DBO exposes statistical, steric, polar and stereoelectronic effects on the hydrogen atom abstraction process in the absence of complications because of competitive exciplex formation.
Abstract: The photophysics of the fluorescent probe Lucifer yellow CH has been investigated using fluorescence spectroscopic and computational techniques. The nonradiative rate is found to pass through a minimum in solvents of intermediate empirical polarity. This apparently anomalous behavior is rationalized by considering the possibility of predominance of different kinds of nonradiative processes, viz. intersystem crossing (ISC) and excited-state proton transfer (ESPT), in solvents of low and high empirical polarity, respectively. The feasibility of the proton transfer is examined by the structure determined by the density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The predicted energy levels based on the time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) method in the gas phase identifies the energy gap between the S1 and nearest triplet state to be close enough to facilitate ISC. Photophysical investigation in solvent mixtures and in deuterated solvents clearly indicates the predominance of the solvent-mediated intramolecular proton transfer in the excited state of the fluorophore in protic solvents.
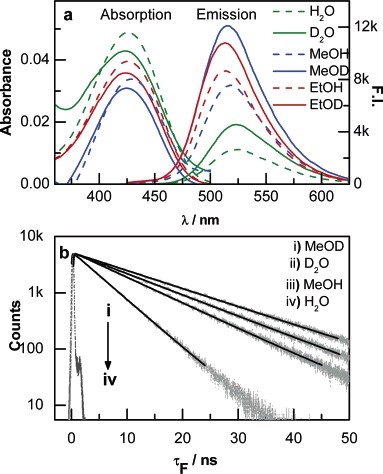
Abstract: A systematic investigation on a broad set of aldehydes reveals that the lifetimes of (Z)-photoenols can be modulated by variation of the substituents. We have found that the lifetimes of (Z)-enols (in benzene) can be varied by more than 1 order of magnitude with a judicious choice of the substituents that exert mesomeric and inductive effects as, for example, in the case of pentamethylbenzaldehyde (ô ) 35 ns) and dicyanomesitaldehyde (ô ) 760 ns). This study thus points to the fact that the electronic factors in conjunction with hydrogen bonding stabilization can considerably broaden the uni- as well as bimolecular chemistry based on photoenolization. Further, we have shown that the photoenols exhibit dramatic shifts in their absorption properties with variation of the substituents; although the photoenols have long been considered to be colored, their absorption properties have not been heretofore comprehensively examined.
Abstract: The complexation of p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene (CX4) with 2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene (1), 2,3- diazabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-2-ene (2), 2,3-diazabicyclo[3.2.2]non-2-ene (3), 1-methyl-4-isopropyl-2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-2-ene (4), and 1-phenyl-2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-2-ene (5) was studied in D2O at pD 7.4 by 1H NMR spectroscopy. The formation of deep inclusion complexes was indicated by large upfield 1H NMR shifts of the guest protons (up to 2.6 ppm), which were also used to assign, in combination with 2D ROESY spectra, a preferential inclusion of the isopropyl group of 4 and a dominant inclusion of the azo bicyclic residue for 5. The bicyclic azoalkanes 1-3 showed
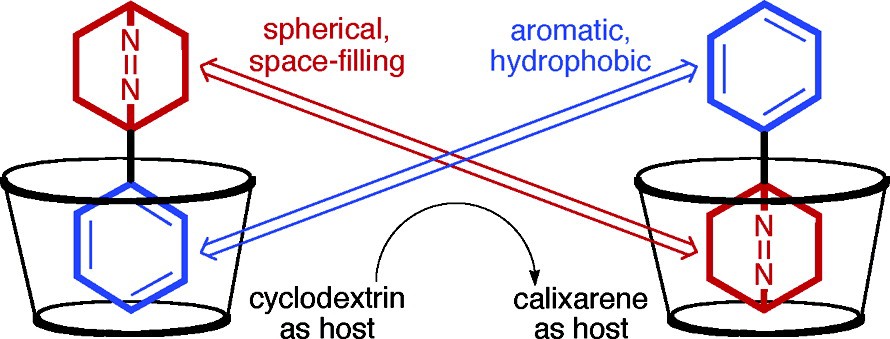
exceptionally high binding constants on the order of 1000 M-1, 1-2 orders of magnitude larger than for previously investigated noncharged organic guest molecules. The strong binding was attributed to the spherical shape complementarity between the guest and the conical cavity offered by CX4. Interestingly, although the derivatives 4 and 5 are more hydrophobic, they showed a 2-3 times weaker binding, which was again attributed to the deviation from spherical shape in these bridgehead-substituted derivatives. The preferential inclusion of the hydrophilic but spherical bicyclic residue of 5 rather than the hydrophobic aromatic phenyl group provides a unique observation in aqueous host-guest chemistry and corroborates the pronounced spherical shape affinity of CX4.
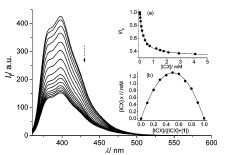
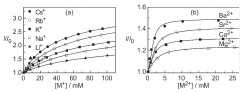
Abstract: A new working principle for detecting inorganic cation binding by water-soluble calix[4]arenes involves the displacement of a fluorescent azoalkane as guest. Fluorescence regeneration is observed for various metal ions, and binding of monovalent cations (alkali and ammonium) to p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene is detected and quantified for the first time.
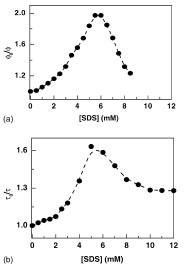
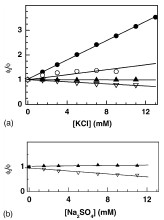
Abstract: Steady state and time resolved ?uorescence measurements have been performed to assess the role of ionic strength and presence of surfactants in the dynamic quenching of 6-methoxyquinoline by halides. The results of quenching by potassium chloride are mainly presented in this paper. The pH dependence of the Stern–Volmer constant has been rationalized in the light of the difference in ionic strengths. The concentration dependent quenching/enhancement of ?uorescence by the surfactant, sodium dodecyl sulphate has been observed and explained by considering an equilibrium between free and bound ?uorophores and modi?cation of critical micellar concentration of SDS by salts. The concentration of the surfactant has been found to affect the quenching/enhancement of ?uorescence by chlorides. Thus, ionic strength and the presence of surfactants are found to be two factors which can affect the sensitivity of the ?uorescent probe towards chlorides.
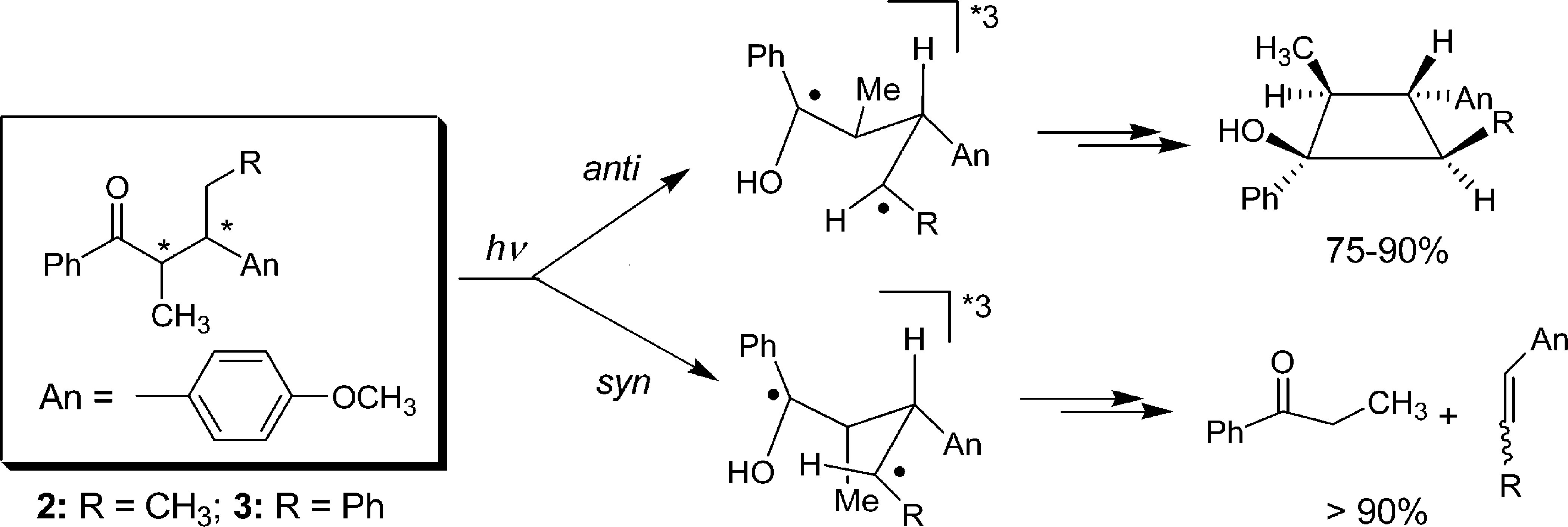
Abstract: The diastereomers of ketones 2 and 3 are shown to exhibit distinct photochemical reactivities due to conformational preferences; while the anti isomers of 2 and 3 undergo efficient Yang cyclization in 75-90% yields with a remarkable diastereoselectivity (> 90%), the syn isomers predominantly undergo Norrish Type II elimination. The differences in the product profiles of the diastereomers are consistent with a mechanistic picture involving the formation of precursor diastereomeric triplet 1,4-biradicals in which the substituents at R and â-positions stabilize the cisoid (cyclization) or transoid (elimination) geometry. The fact that such a diastereomeric relationship does indeed ensue at the triplet-excited-state itself is demonstrated via the nanosecond laser-flash photolysis of model ketones 1. The diastereomeric discrimination in the product profiles observed for ketones 2 and 3 as well as in the triplet lifetimes observed for ketones 1 can both be mechanistically traced back to different conformational preferences of the groundstate diastereomeric ketones and the intermediary 1,4-biradicals. Additionally, it emerges from the present study that the syn and anti diastereomers of ketones 2 and 3 represent two extremes of a broad range of widely examined butyrophenones, which lead to varying degrees of Yang photocyclization depending on the alkyl substitution pattern.
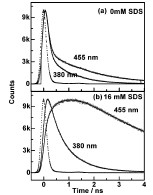
Abstract: The effect of micellar environment on the excited state proton transfer (ESPT) of 2-(2‘-pyridyl)benzimidazole (2PBI) has been investigated by steady state and time resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. The ESPT, which occurs to a rather small extent at pH 7, is found to be enhanced remarkably at the interface of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) micelles and water. Such an enhancement is not observed for the cationic cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) or neutral Triton X-100 micelles. This selective enhancement is explained in the light of a modification of pKa and a more acidic local pH in the micelle-water interface. A rise time of about 890 ps is observed in the region of tautomer emission. The origin of this rise time is explored, considering three factors, namely, diffusion controlled protonation of the normal form of 2PBI, slow and possibly incomplete solvation of the transition state, leading to a slowing down of the proton transfer process and a similar slow dynamics of the tautomeric excited state.
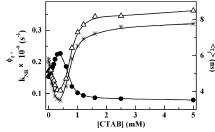
Abstract: The interaction of the ?uorophore Lucifer yellow with micelles has been monitored using steady state and time resolved ?uores- cence techniques. Contrary to the popular belief that the ?uorophore is too polar to associate with the stern layer or hydrophobic core of micelles, we have observed that it binds with the micelles of the positively charged surfactant cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and that such interaction causes an decrease in the rates of its non-radiative processes. This phenomenon cannot be explained solely in the light of a reduced polarity, as we have demonstrated that the photophysics of Lucifer yellow is complex and intramolecular charge transfer does not seem to be the only excited state process that is operative.
Abstract: Supramolecular radiative decay engineering allows systematic variations of the radiative decayrates, and therefore changes in the fluorescence lifetimes and intensities. Depending on whetherfluorescent dyes are immersed in macrocyclic host molecules with low or high polarizability, reducedor enhanced fluorescence lifetimes may result. Solvatochromic probes to “measure” thepolarizability inside such molecular container compounds are now at hand. Cucurbiturils, for example,are water-soluble host molecules, which possess a cavity with an exceptionally low polarizability,close to the gas phase. Placing fluorescent dyes inside cucurbiturils allows one to create in aqueoussolution a unique microenvironment, which approaches that of the gas phase and leads to unprecedentedphotophysical behavior. Accordingly, complexation by cucurbituril leads to prolonged fluorescencelifetimes, for 2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-2-ene (DBO) up to 1?µs, the same as that foundin the gas phase.
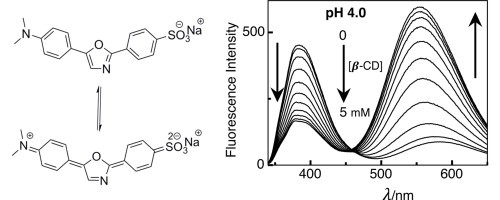
Abstract: pH dependent encapsulation of dapoxyl sodium sulfonate (DSS), a charge transfer (CT) dye, with α- and β-cyclodextrin (CD), macrocyclic molecules made up with sugar units, has been performed using steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence measurements; both confirm the formation of an efficient inclusion complex with both non-protonated and protonated form of DSS. Moreover, the fluorescence intensity is affected due to modulation of acid-dissociation constant by CD encapsulation as a consequence of preferential binding affinities with different prototopic forms of DSS. In particular, we observed that the relocation of DSS from water into the less polar hydrophobic cavity of CD causes huge fluorescence enhancement in water. Our investigation reveals that the micro-polarity inside β-CD cavity is akin to methanol–water (1:1) mixtures.
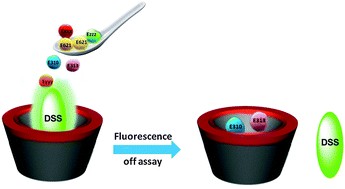
Abstract: Host–guest complexation of dapoxyl sodium sulphonate (DSS), an intramolecular charge transfer dye with water-soluble and non-toxic macrocycle γ-cyclodextrin (γ-CD), has been investigated in a wide pH range. Steady-state absorption, fluorescence and time-resolved fluorescence measurements confirm the positioning of DSS into the hydrophobic cavity of γ-CD. A large fluorescence enhancement ca. 30 times, due to 1 : 2 complex formation and host-assisted guest-protonation have been utilised for developing a method for the utilisation of CD based drug-delivery applications. A simple fluorescence-displacement based approach is implemented at physiological pH for the assessment of binding strength of pharmaceutically useful small drug molecules (ibuprofen, paracetamol, methyl salicylate, salicylic acid, aspirin, and piroxicam) and six important antibiotic drugs (resazurin, thiamphenicol, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, kanamycin, and sorbic acid) with γ-CD.
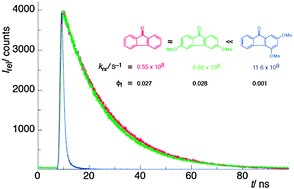
Abstract: A comprehensive investigation of the photophysics of a broad set of fluorenones substituted with methoxy groups at different positions brings out the importance of the location of substituents on the fluorenone core in modulating fluorescence and radiationless deactivation by way of modification of the singlet-excited state energy and its character. While the substituents at para positions are found to affect neither the fluorescence quantum yield nor the lifetime, those at meta positions are found to significantly modify the latter. A cumulative effect is observed for the substituents in that the nonradiative decay (knr) becomes progressively dominant with an increasing number of meta-methoxy substituents. For example, the trimethoxy substitution in 2,4,7-trimethoxyfluorenone (8) is found to increase knr by ca. 30 fold relative to that of the parent fluorenone (1) in a polar aprotic solvent such as acetonitrile. The predominance of nonradiative decay (knr) is rationalized from stabilization of the singlet-excited state via partial charge transfer from meta-methoxy substituents to the carbonyl group. Accordingly, a nice correlation is observed for the nonradiative (knr) rate constants versus singlet-excitation energies derived from fluorescence emission maxima of all fluorenones in acetonitrile. The macrocyclic host cucurbit[7]uril (CB7) is found to not only enhance the fluorescence of the parent fluorenone (1) significantly, but also increase the singlet lifetime considerably. Based on the changes observed in the absorption spectra and the lifetimes determined, a 1 : 1 host–guest complex has been proposed with CB7. The fluorescence lifetime observed in the presence of CB7 suggests that the hydrophobic fluorenone (1) can be employed as a probe to report on a polar microenvironment shielded from hydrogen bonding interactions in a polar protic solvent.
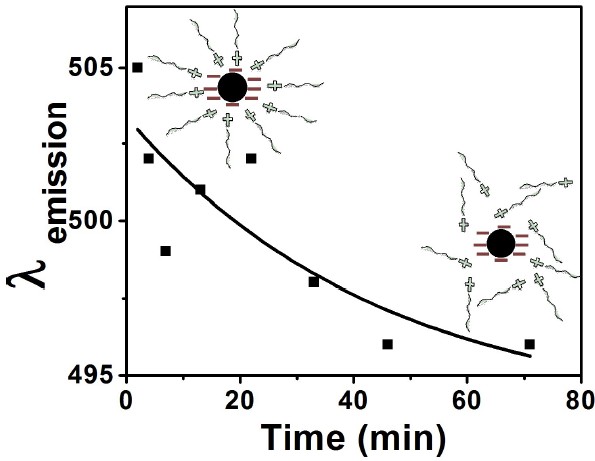
Abstract: We have recently reported the synthesis of water-dispersible, polymer-passivated and redox-active carbon quantum dots (CQDs). The CQDs were converted into a solvent-less conductive fluid through a step-wise surface modification technique. The material has a core-corona-canopy structure with CQD as core, passivating-polymer as corona and polyetheramine (Jeffamine®) as canopy. These materials are unique in characteristics and are designated as nano-ionic materials (NIMs). Structure and properties of CQD-NIMs were determined with dynamic light scattering, thermogravimetry, differential scanning calorimetry, photoluminescence (PL) and cyclic voltammetry (CV). Dynamic changes in extrinsic PL maxima (?em) of the CQDs were observed during and after CV. Such fluctuations in ?em helped to understand the sequential ordering and disordering of Jeffamine® canopy on the CQD surface during polarization during CV. The phenomenon enables us to understand molecular canopy dynamics in NIMs and further showcase redox-active CQDs as a sustainable material for future electrochemical applications.
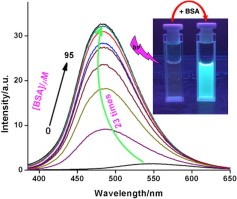
Abstract. Synthesis, single-crystal X-ray characterization, and spectroscopic investigation of small, non-charged diethyl 6-(dimethylamino)naphthalene-2,3-dicarboxylate (DMNDC) by UV-Visible, steady-state, and time-resolved fluorescence reveal a series of interesting photophysical properties originating from the intrinsic intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) state, leading to diverse applications. Stokes shift, lifetime, and emission maxima of DMNDC show a very good correlation with ET(30) solvent polarity scale for a series of different polarity solvents, confirms that it has very good environment sensitivity. Furthermore, this dye has been found to be an exceptionally suitable probe for determining critical micelle concentration (CMC) and probing self-organization processes of five different type of surfactant with structural diversity. A 20-60 nm blue shift in emission maxima accompanied by a large fluorescence lifetime enhancement (ca. 23 ns) was observed upon relocation of DMNDC into a hydrophobic microenvironment. Along with this, the small size, electroneutrality, pH stability, and excellent solvatochromic fluorescent properties are employed for deciphering the number of hydrophobic binding pockets with strong affinity and their local microenvironment present in Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA).
Abstract: An ultrasensitive ratiometric fluorescent sensor made of an N,N-dimethylaminonaphthalene anhydride moiety for detection of aliphatic primary amines is reported. Biogenic amines at nanomolar concentration is detected with the additional ability to discriminate between primary, secondary and tertiary amines by using both UV-Visible and fluorescence spectroscopy.
Abstract: pH dependent host–guest complexation of dapoxyl sodium sulfonate (DSS), an intramolecular charge transfer dye, with 2-hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin (HP-ß-CD) has been investigated. Complexation of DSS with HP-ß-CD has been studied at four different pH values using steady-state and time-resolved spectroscopy. Cyclodextrin encapsulation alters the acid–base properties of DSS and results in host-induced deprotonation. A large fluorescence enhancement of DSS was observed upon HP-ß-CD binding at different pH values and it enabled us to evaluate the pH dependent binding affinity of DSS with HP-ß-CD. The binding affinity of non-protonated DSS was much higher when compared to its protonated state. Subsequently, the encapsulation induced fluorescence enhancement at ca. pH 7.0 has been implemented for developing a fluorescence displacement method for assaying the binding affinity of food-additives namely monosodium glutamate, trans-ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, gallic acid and its methyl, ethyl and propyl ester derivatives with HP-ß-CD. Other than monosodium glutamate, all other tested food-additives show preferential binding to the hydrophobic cavity of HP-ß-CD. Therefore, this quick method of assaying the binding affinity of food additives with a water-soluble macrocyclic host molecule can offer better food processing ability, controlled release, and stability.
Abstract: Iridium-based metal complexes containing polypyridyl-pyrazine ligands show properties of DNA intercalation. They serve as roadblocks to DNA polymerase activity, thereby inhibiting the polymerization process. Upon the addition of increasing concentrations of these iridium complexes, a rapid polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assay reveals the selective inhibition of the DNA polymerization process. This label-free approach to study the inhibition of fundamental cellular processes via physical roadblock can offer an alternative route toward cancer therapy.
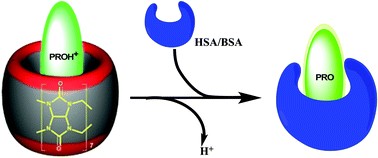
Abstract: Small drug molecules and other important metabolites are delivered via a suitable carrier protein-mediated transport through a specific receptor. The process is highly coordinated and associated with complexation induced properties of deliverable molecules. To get a molecular insight, in this report, we tried to mimic the delivery process to know how the carrier protein relocates the drug molecule from the macrocyclic host cavity to its binding pocket and how the electronic and the chemical properties of the guest get altered. Bovine and human serum albumin (BSA and HSA) were used as the model carrier proteins which can snatch out 6-propanoyl-2-(N,N-dimethylamino)naphthalene (PRO), dye used as a drug model (known to bind at the drug-binding pocket of the carrier protein), from the cucurbit[7]uril (CB7) cavity, a potential drug delivery carrier. Prior to performing the fluorescence-based bio-supramolecular relocation assay using BSA and HSA, CB7 and PRO, we have investigated the effect of CB7 encapsulation and protonation on the fluorescence properties of PRO. A significant shift in the pKa value from 3.4 to 6.6 (ca. 3.2 logarithmic units) of PRO was observed upon encapsulation with CB7, which causes a huge fluorescence quenching even at neutral pH. The binding affinity of protonated and neutral PRO for CB7 also confirms a 3.2 unit shift in the acid-dissociation constant. A displacement assay using a strong CB7 binder, viz., 1,6-diaminohexane, confirms encapsulation of PRO in the CB7 cavity. Encapsulation of neutral PRO by CB7 shows a significant fluorescence enhancement accompanied by a ~35 nm blue shift in the emission maxima.